It’s easy to get confused between them since some people use them interchangeably. These chemicals have a role in critical physiological functions and have been related to improved metabolism, energy, and cellular repair. This article will explain the differences between NMN and NAD, as well as their possible advantages and contributions to the promotion of healthy aging.
** This post may contain affiliate ads where we make a small commission on purchases made at no cost to you. We only recommend products we think you will find valuable.**
NMN vs. NAD: What’s the difference?
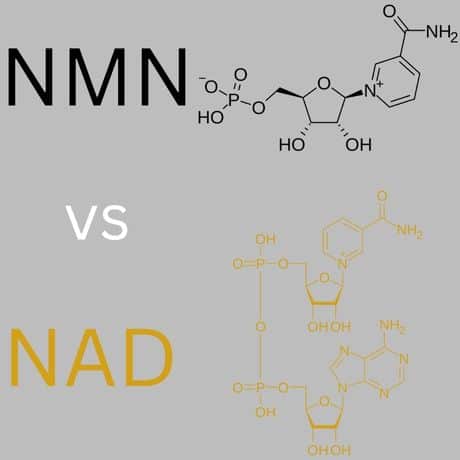
NAD is an active coenzyme that takes part in numerous metabolic processes throughout the entire body. NMN, on the other hand, is a precursor molecule to NAD. This means NMN is converted to NAD in your cells through a chemical process.
NMN is thought to be more easily absorbed by the body due to natural pathways in the cells that allow it to be absorbed and then converted to NAD. NAD doesn’t have a direct way of entering the cells, so it must be converted to NMN or Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) before it can be absorbed and then once again converted into NAD once in the cell.
Both NMN and NAD are crucial for cellular functions, including energy consumption and cellular repair. On the surface, their functions look the same but have some significant differences. NMN is thought to have more physical effects, and NAD is thought to have more effect on mental health and brain health.
We think that NMN is the better option to supplement between the two of them. We’ll cover what NMN does better than NAD, and why you should start thinking about adding an NMN supplement to your daily routine.
What is NMN?
NMN stands for Nicotinamide mononucleotide. It is a chemical found naturally in the body and involved in several cellular functions, including energy metabolism and DNA repair. NMN is a precursor to the coenzyme NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is involved in many metabolic processes in the body.
In biology, a precursor refers to a substance that can be transformed into another substance. In the context of NAD+ and NMN, NMN gets converted into NAD+ after it enters the cells. Basically, NMN serves as a building component for the creation of NAD+.
NMN has attracted attention recently due to its potential anti-aging benefits and capacity to raise NAD+ levels. Interest in NMN has also increased due to the promise of NMN being a more efficient way of raising NAD levels versus a NAD supplement.
NMN supplements have been studied for their potential to increase NAD+ levels, improve cellular function, and reduce age-related cellular damage.
If you want to learn even more, check out our full breakdown of NMN.
What does NMN do for the body?
NMN increases the body’s NAD concentrations through its ability to convert into NAD. We briefly covered some of the various health benefits above, so let’s take a little bit of a deeper look. Because NAD is vital to the production of energy, the increased NAD levels enable the more efficient conversion of food into energy, resulting in higher cellular energy levels.
The improved energy production that results from increasing your NAD levels may also help offset age-related metabolic efficiency declines. By increasing NAD levels, NMN supplementation is also believed to help negate the age-related cognitive decline that occurs with age.
Research also suggests that NMN supplementation can decrease inflammation in the body.
One rodent study looked at the effects of NMN supplementation on age-related inflammation. The results showed that a daily NMN supplement could help reduce inflammation in the liver and adipose tissue. The researchers hypothesized that this might be the result of NMNs’ ability to inhibit the factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which is a major mediator of inflammation.¹
Another study, this time with human subjects, looked at the effects of NMN supplementation on cardio function and inflammation. The results showed that NMN supplementation was able to reduce the inflammatory biomarker interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the blood.²
These studies suggest that NMN supplementation has anti-inflammatory properties. However, more research is needed to fully comprehend the specific mechanism of this. Decreased inflammation in the body can have a wide range of favorable consequences, including increased immunological function, better heart health, lower risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer, improved joint health and mobility, and improved mental health. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes long-term, it can lead to tissue damage and a range of health concerns. By reducing inflammation with the use of an NMN supplement, you may be able to improve your general health and well-being.
NMN Benefits
NMN and NAD have similar benefits, playing crucial roles in cellular functions like energy metabolism and cellular repair. Although there is more research that has to be done, there have been some differences identified.
The main NMN Benefits are:
-
Improved cardiovascular health: Improvements in arterial function and inflammation has been linked to NMN, helping to support cardiovascular health.³
-
Improved insulin sensitivity: NMN has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity, which may help manage and prevent type 2 diabetes.⁴
-
Anti-aging effects: NMN supports cellular repair, metabolism, and energy generation. These effects help to offset age-related health decline.⁵
If you want to know more, take a look at our article on the benefits of NMN.
Premium NMN Supplement
 Wonderfeel Youngr
Wonderfeel Youngr
Youngr™ NMN is a patented solution to aging. Formulated with emergent antioxidants and sirtuin activation, it uses a multi-targeted approach to defend and slow down biological aging at the cellular level…
CHECK PRICE
Recommended Dosage of NMN
NMN dose recommendations may change based on a number of variables, including age, weight, and general health. Since NMN is regarded as a dietary supplement and is not overseen by the FDA, there is no set daily intake recommendation.
Studies have used doses ranging from 100 to 900 mg per day. Most generic supplement product labels recommend dosages between 250 and 500 mg daily. However, brands on the cutting edge of this space such as Wonderfeel, world renowned doctors such as David Sinclair and Andrew Salzman, plus the latest human clinical study recommend higher dosages to realize the most benefits.⁶ You can start with a lower amount to assess your body’s tolerance then move up to the 600-900mg daily range.

Side Effects of NMN
NMN is generally considered safe when taken within the recommended dosages. However, some people may experience minor negative side effects, including:
-
Gastrointestinal issues: Some people may have stomach distress, nausea, or diarrhea while taking large dosages of NMN.
-
Skin irritation or flushing: Excessive NMN dosages may result in skin redness or flushing, especially on the face and neck.
-
Headaches: Using NMN supplements may cause headaches or migraines.
-
Insomnia or sleep disturbances: NMN supplements may interfere with sleep for some people.
-
Allergic reactions: In rare situations, some people may develop allergic reactions to NMN supplements. This may cause such reactions as itching, hives, or breathing difficulty.
Best way to take NMN
NMN supplements are sold in a variety of formats, including capsules, tablets, powders, and sublingual tablets. The most popular forms are capsules and tablets, which are normally taken orally with water.
Powders can be mixed with the liquid of your choice and consumed orally, while sublingual pills are put under the tongue and allowed to dissolve.
There is no universal agreement regarding the optimal NMN supplement because it mostly depends on personal preference and convenience. Some anecdotes claim that sublingual pills may have a higher bioavailability and quicker absorption compared to other NMN supplement formulations, but more research is needed to confirm this.

What is NAD?
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme that is present in all living cells. It is essential for several metabolic functions, including converting food into energy, repairing damaged DNA, and controlling gene expression.
Naturally declining NAD levels may play a role in age-related illnesses and cognitive impairment. NAD supplements are used to raise NAD levels in the body and have been researched for their possible health advantages, such as enhanced cognitive function, higher energy, and anti-aging effects.
NAD Benefits
The main benefits of NAD are:
-
Greater energy production: NAD plays a critical role in energy production throughout the body, particularly in the synthesis of ATP, the chemical that delivers energy to cells.⁷
-
DNA repair: NAD participates in DNA repair procedures, which can lessen the risk of cellular damage and mutations that could cause cancer and other diseases.⁸
-
Increased cognitive function: NAD has been associated with better cognitive performance and may help to prevent age-related cognitive decline.⁹
Recommended Dosage of NAD
There is also no official dosage recommendation when it comes to NAD. Clinical studies have used similar amounts to NMN, and most manufacturers of NAD supplements suggest a dosage range of 200-300 mg daily.
What does NAD do for the body?
The key functions of NAD in the body are:
-
Energy production: NAD is involved in the process of transforming food into energy. It is a crucial part of the electron transport chain, which creates ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the chemical that powers cellular energy. The increased energy levels that result can help to offset age-associated weight gain.¹⁰
-
DNA repair: NAD is also involved in repairing damaged DNA. It helps to activate enzymes that repair DNA damage produced by environmental causes, such as radiation and chemicals.¹¹
-
Gene expression: NAD is involved in the control of gene expression, which is the mechanism by which genes are active or inactive. NAD controls some proteins that regulate gene expression.¹²
-
Cognitive benefits: NAD has also been researched for its possible neuroprotective properties. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are two neurodegenerative conditions that it may help to fend against.¹³
-
Anti-aging effects: NAD levels typically fall as we age, and this decline has been connected to age-related disorders and cognitive loss. Supplemental NAD has been studied for its ability to help offset age-related health decline.¹⁴
Side Effects of NAD
NAD is generally considered safe when taken within the same dosages as NMN. However, some people may experience minor negative side effects, including:
-
Gastrointestinal issues: Some people may have stomach distress, nausea, or diarrhea while taking large dosages of NAD.
-
Skin irritation or flushing: Excessive NAD dosages may result in skin redness or flushing, especially on the face and neck.
-
Headaches: Using NAD supplements may cause headaches or migraines.
-
Insomnia or sleep disturbances: NAD supplements may interfere with sleep for some people.
-
Allergic reactions: In rare situations, some people may develop allergic reactions to NAD supplements. This may cause such reactions as itching, hives, or breathing difficulty.
Best way to take NAD
Just like NMN, NAD supplements are sold in a variety of formats, including capsules, tablets, powders, and sublingual tablets. The most popular forms are capsules and tablets, which are normally taken orally with water.
The most effective way to take NAD is intravenous, but there are a few factors that also make it the most difficult option. Intravenous NAD is more expensive, as well as being almost impossible to receive daily treatments.
Due to the relatively poor absorbability of NAD through oral routes, you would be better off going with an NMN supplement.
What happens when NAD levels drop?
NAD levels normally fall with age, and this decline has been connected to several undesirable effects on the body, including:
-
Decreased energy production: NAD is needed for the process of turning food into energy. This process may become less effective at low NAD levels, resulting in fatigue and poor physical performance. The mitochondria are the cell’s energy factories, and low NAD levels can result in mitochondrial dysfunction.
-
DNA damage: NAD is involved in repairing damaged DNA. Low NAD levels can cause DNA damage to build up and increase the risk of developing cancer and other disorders.
-
Age-related disorders: Decreased NAD levels have been associated with age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. NAD supplements have been studied for their potential to protect against these diseases by improving cellular function and reducing cellular damage.
-
Cognitive impairment: Age-related cognitive impairment correlates with a natural fall in NAD levels as people age. Supplemental NAD has been investigated for its potential to improve the health of brain cells and enhance cognitive function in older adults.
-
Decreased exercise capacity: NAD is involved in the process of creating energy for physical activity. Low NAD levels can affect a person’s ability to work out with full intensity, in part due to a decline in skeletal muscle mass and strength.
Premium NMN Supplement
 Wonderfeel Youngr
Wonderfeel Youngr
Youngr™ NMN is a patented solution to aging. Formulated with emergent antioxidants and sirtuin activation, it uses a multi-targeted approach to defend and slow down biological aging at the cellular level…
CHECK PRICE
What can I do to help boost NAD levels naturally?
There are a number of lifestyle choices that will help to boost your NAD levels naturally, including:
1. Diet
Eating a balanced, healthy diet that includes foods rich in niacin, such as meat, fish, poultry, and whole grains. If meal prepping is keeping you from a healthy diet, you can check out a meal delivery service such as Trifecta Meals.
Niacin-rich foods can naturally raise NAD+ levels when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Niacin, also referred to as vitamin B3, is a necessary nutrient that is important for NAD+ metabolism.
The NAD+ salvage route is one of the main mechanisms through which niacin raises NAD+ levels. Niacin is transformed into nicotinamide in this pathway, and nicotinamide is then utilized to create NAD+. The majority of cells in the body go through this process, which is crucial for keeping NAD+ levels stable.
Niacin has been shown to provide a number of health advantages in addition to raising NAD+ levels, including lowering inflammation, enhancing blood lipid profiles, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Niacin side effects include flushing, itching, and digestive problems can also occur at high doses.¹⁵
2. Exercise
Participating in frequent physical activity has been shown to raise NAD levels. A critical enzyme in the NAD+ salvage pathway known as nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) has been demonstrated to be upregulated by exercise. Nicotinamide is recycled in the NAD+ salvage pathway to create NAD+. NAD+ production rises as a result of increased NAMPT expression during exercise.
Physical exercise has shown the potential to boost mitochondrial biogenesis, which is the process of making new mitochondria. The mitochondria are the center of the cell and are crucial for the metabolism of energy. Because of the increased demand for NAD+ during mitochondrial respiration, NAD+ levels rise during mitochondrial biogenesis.¹⁶
3. Sleep
Getting enough sleep, which has been linked to increased NAD levels. The NAD+ salvage pathway’s main enzyme, NAMPT, has been found to express itself more frequently during sleep. By a process known as the NAD+ salvage pathway, nicotinamide is recycled to create NAD+. During sleep, NAMPT expression rises, which increases NAD+ synthesis.¹⁷
DNA repair, a crucial process for preserving genomic stability, is aided by sleep. NAD+ serves as a cofactor for DNA repair, and sufficient amounts of NAD+ are necessary for effective DNA repair. NAD+ levels rising while you sleep may therefore facilitate DNA repair.
4. Stress Reduction
Reducing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga can assist in sustaining healthy NAD levels. Increased inflammation brought on by long-term stress can lower NAD levels. Lowering stress can help reduce inflammation, which will raise levels of NAD.¹⁸ NAMPT is demonstrated to be expressed at higher levels in response to reduced stress. The recycling of nicotinamide to create NMN, which is then used to create NAD+, is known as the NAD+ salvage route. When stress is reduced, NAMPT expression rises, which increases NMN production.¹⁹
5. Minimize Alcohol Consumption
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, which can deplete NAD levels in the liver. Alcohol has also been shown to have a negative effect on NMN synthesis. That’s because it decreases levels of NAMPT. Alcohol consumption may also increase oxidative stress levels. The free radical damage that results from oxidative stress contributes to the depletion of both NMN and NAD levels in the body.²⁰
6. Fasting
Some studies show that fasting, or calorie restriction, increases NAD levels. Calorie restriction and fasting have both been shown to stimulate the body to produce more NMPT. This, in turn, leads to increased NAD levels. Calorie restriction has also been shown to activate SIRT1, a protein deacetylase that is essential for NAD+ metabolism. NAD+ levels increase as a result of SIRT1 enhancing NAD+ production and activating NAMPT.²¹
It has been demonstrated that fasting or calorie restriction improves mitochondrial activity, which is accompanied by an increase in NAD+ levels because mitochondrial respiration places a greater demand on NAD+. The mitochondria are the heart of the cell and are crucial for the metabolism of energy. By improving mitochondrial performance through fasting or calorie restriction, NAD+ levels can increase as a result of an increase in NAD+ demand.²²
NMN Supplements Vs. NAD Supplements
Throughout this article, we have seen that both NMN and NAD have similar benefits for the body, including boosting energy levels, repairing damaged DNA, and offsetting the effects of aging. When it comes to choosing just one as a supplement, though, we believe that NMN is the better option.
Research shows that NMN supplements are better absorbed into the body than NAD supplements. Because NMN is a direct precursor to NAD and can quickly transform into NAD in the body, studies have shown that NMN is more readily absorbed through cell membranes than NAD. Orally administered NMN, but not NAD itself, significantly raised NAD levels in mice, according to a 2022 study that appeared in the journal npj Aging.²³
The most effective way to take NAD in terms of absorbability is intravenously. This is obviously not a viable option for the vast majority of people.
When it comes to choosing an NMN supplement, there are many brands to choose from. While it may seem that all NMN supplements are pretty much alike, that is certainly not the case. When purchasing an NMN supplement, there are a few important factors that you should take into account.
Find a product that uses pure, high-quality NMN. Also, the dosage must be taken into account because supplements may differ in their NMN content. Choose a product whose serving size and NMN content are both specified. You should look for a supplement whose efficacy and purity have been independently verified by a 3rd party laboratory. This guarantees that the product you receive is of high quality and that it contains what it says it does. Consider the supplement’s form as well; some people might like capsules, whereas others might prefer powders or sublingual tablets.
Having extensively researched the NMN supplement market, we recommend Wonderfeel Youngr. Every capsule of Wonderfeel Youngr contains 450 mg of activated NMN. Non-activated NMN supplements include the NMN molecule in its unaltered state, while activated NMN supplements have an extra chemical group bonded to the NMN molecule to boost its absorption and effectiveness.
Wonderfeel Youngr also contains 2 mg of ergothioneine, which is a vitamin with research supporting its anti-aging benefits, and 10 mcg of energy-boosting vitamin D. The ingredients are contained in a vegan capsule. This supplement is also 3rd party tested for purity and potency.

Summary
There have been some very exciting developments in the area of anti-aging research over the past few years. This has led to an increase in the popularity of certain supplements, including NMN and NAD. Both of them are able to increase the body’s NAD levels, which naturally decline with age.
However, taking an NMN supplement has been shown to do so faster and more effectively. So, when it comes to deciding between an NMN and a NAD supplement, we recommend that you opt for NMN.
The best NMN supplement in the current market is Wonderfeel Youngr, which provides 900 grams of activated NMN per serving and other proven anti-aging ingredients. This product is also 3rd party tested for purity and potency.
- Mills, Kathryn F., et al. “Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice.” Cell Metabolism, vol. 24, no. 6, Dec. 2016, pp. 795–806
- Liu, Jing, et al. “Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Decreasing COX-2 Expression in Macrophages.” Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, vol. 8, 6 July 2021, p. 702107
- Wei, Zisong, et al. “Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: An Emerging Nutraceutical against Cardiac Aging?” Current Opinion in Pharmacology, vol. 60, 1 Oct. 2021, pp. 291–297
- Yoshino, Mihoko, et al. “Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Increases Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in Prediabetic Women.” Science, 22 Apr. 2021
- Shade, Christopher. “The Science behind NMN–a Stable, Reliable NAD+Activator and Anti-Aging Molecule.” Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal, vol. 19, no. 1, 1 Feb. 2020, pp. 12–14
- Yi, Lin, et al. “The Efficacy and Safety of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Supplementation in Healthy Middle-Aged Adults: A Randomized, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Dose-Dependent Clinical Trial.” GeroScience, 8 Dec. 2022
- Cuenoud, Bernard, et al. “Brain NAD Is Associated with ATP Energy Production and Membrane Phospholipid Turnover in Humans.” Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, vol. 12, 16 Dec. 2020
- Croteau, Deborah L., et al. “NAD+ in DNA Repair and Mitochondrial Maintenance.” Cell Cycle, vol. 16, no. 6, 10 Feb. 2017, pp. 491–492
- Campbell, Jared M. “Supplementation with NAD+ and Its Precursors to Prevent Cognitive Decline across Disease Contexts.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 15, 7 Aug. 2022, p. 3231
- Cuenoud, Bernard, et al. “Brain NAD Is Associated with ATP Energy Production and Membrane Phospholipid Turnover in Humans.” Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, vol. 12, 16 Dec. 2020
- Croteau, Deborah L., et al. “NAD+ in DNA Repair and Mitochondrial Maintenance.” Cell Cycle, vol. 16, no. 6, 10 Feb. 2017, pp. 491–492
- Covarrubias, Anthony J., et al. “NAD+ Metabolism and Its Roles in Cellular Processes during Ageing.” Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, vol. 22, no. 2, 22 Dec. 2020, pp. 119–141
- Campbell, Jared M. “Supplementation with NAD+ and Its Precursors to Prevent Cognitive Decline across Disease Contexts.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 15, 7 Aug. 2022, p. 3231
- Liu, Xuqian, and Taosheng Huang. “The Role of NAD+ in Anti-Aging Therapies.” American Journal of Biomedical Science & Research, vol. 6, no. 5, 20 Dec. 2019
- Gasperi, Valeria, et al. “Niacin in the Central Nervous System: An Update of Biological Aspects and Clinical Applications.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 20, no. 4, 23 Feb. 2019
- Bishop, David J., et al. “High-Intensity Exercise and Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Current Controversies and Future Research Directions.” Physiology, vol. 34, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2019, pp. 56–70
- Tokizane, Kyohei, and Shin-ichiro Imai. “NAD+ Oscillation and Hypothalamic Neuronal Functions.” Faculty Reviews, vol. 10, 27 Apr. 2021
- Picard, Martin, and Bruce S. McEwen. “Psychological Stress and Mitochondria.” Psychosomatic Medicine, vol. 80, no. 2, 2018, pp. 141–153
- Galli, Ubaldina, et al. “Medicinal Chemistry of Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) Inhibitors.” Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, vol. 56, no. 16, 31 May 2013, pp. 6279–6296
- French, Samuel W. “Chronic Alcohol Binging Injures the Liver and Other Organs by Reducing NAD+ Levels Required for Sirtuin’s Deacetylase Activity.” Experimental and Molecular Pathology, vol. 100, no. 2, Apr. 2016, pp. 303–306
- Cantó, Carles, et al. “Interdependence of AMPK and SIRT1 for Metabolic Adaptation to Fasting and Exercise in Skeletal Muscle.” Cell Metabolism, vol. 11, no. 3, Mar. 2010, pp. 213–219
- Lettieri-Barbato, Daniele, et al. “Time-Controlled Fasting Prevents Aging-like Mitochondrial Changes Induced by Persistent Dietary Fat Overload in Skeletal Muscle.” PLOS ONE, vol. 13, no. 5, 9 May 2018, p. e0195912
- Igarashi, M., Nakagawa-Nagahama, Y., Miura, M. et al. Chronic nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation elevates blood nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels and alters muscle function in healthy older men. npj Aging 8, 5 (2022).