by Faculty of California – San Diego
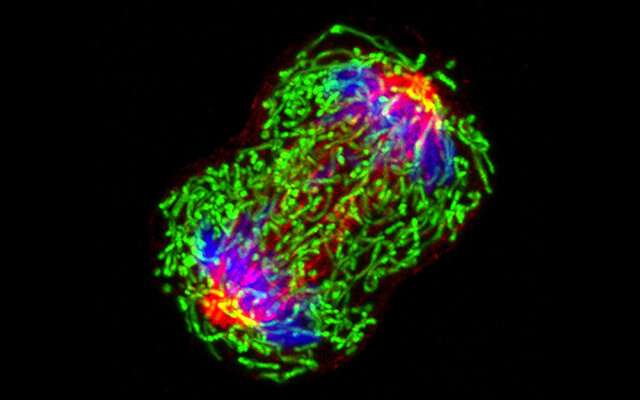 A breast most cancers cell captured throughout the technique of division, with tubulin (a structural protein) in purple; mitochondria in inexperienced; and chromosomes in blue. Credit score rating: Wei QianNational Most cancers Institute
A breast most cancers cell captured throughout the technique of division, with tubulin (a structural protein) in purple; mitochondria in inexperienced; and chromosomes in blue. Credit score rating: Wei QianNational Most cancers Institute
Breast most cancers and type 2 diabetes would look like distinctly completely completely different sicknesses, with commonality solely of their commonality. Breast most cancers is the second most recognized malignancy after some types of pores and pores and skin most cancers; roughly 1 in eight U.S. ladies will develop invasive breast most cancers over the course of their lifetime. Larger than 10 p.c of the U.S. inhabitants has diabetes, with an estimated 2 in 5 People anticipated to develop the facility sickness all through their lifetime.
Nonetheless, earlier evaluation has uncovered associations between the two sicknesses. Women with diabetes, as an illustration, have a 20 to 27 p.c elevated risk of making breast most cancers. Insulin resistance—a key attribute of diabetes—has been associated to breast most cancers incidence and poor survival. Inhabitants analysis suggest diabetes risk begins to increase two years after a breast most cancers evaluation, and by 10 years post-diagnosis, the possibility is 20 p.c elevated in breast most cancers survivors than in age-matched ladies with out breast most cancers.
Nonetheless these epidemiological linkages are often not clear-cut or definitive, and some analysis have found no associations the least bit. In a model new paper, publishing Might 30, 2022 in Nature Cell Biology, a evaluation group led by scientists at Faculty of California San Diego School of Medicine describe a possible natural mechanism connecting the two sicknesses, whereby breast most cancers suppresses the manufacturing of insulin, resulting in diabetes, and the impairment of blood sugar administration promotes tumor improvement.
“No sickness is an island because of no cell lives alone,” acknowledged corresponding analysis creator Shizhen Emily Wang, Ph.D., professor of pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine. “On this analysis, we describe how breast most cancers cells impair the function of pancreatic islets to make them produce a lot much less insulin than wished, leading to elevated blood glucose ranges in breast most cancers victims compared with females with out most cancers.”
Wang acknowledged the analysis was impressed by early work and steering from Jerrold Olefsky, MD, professor of medication and affiliate dean for scientific affairs throughout the Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism at UC San Diego School of Medicine. Olefsky is co-senior creator of the analysis with Wang.
The perpetrator, in accordance with Wang and Olefsky, are extracellular vesicles (EV)—gap spheres secreted or shed by cells that transport DNA, RNA, proteins, fats and completely different provides between cells, a type of cargo communication system.
On this case, the most cancers cells had been found to be secreting microRNA-122 into the vesicles. Wang acknowledged when vesicles attain the pancreas, they’ll enter the islet cells answerable for insulin manufacturing, dispense their miR-122 cargo and harm the islets’ essential function in sustaining a regular blood glucose stage.
“Most cancers cells have a sweet tooth,” Wang acknowledged. “They use further glucose than healthful cells in an effort to fuel tumor improvement, and this has been the thought for PET scans in most cancers detection. By rising blood glucose which may be merely utilized by most cancers cells, breast tumors make their very personal favorite meals and, within the meantime, deprive this vital nutrient from common cells.”
The evaluation was carried out using mouse fashions, which found that slow-releasing insulin pellets or a glucose-lowering drug known as an SGLT2 inhibitor restored common administration of glucose throughout the presence of a breast tumor, which in flip suppressed the tumor’s improvement.
“These findings assist a greater need for diabetes screening and prevention amongst breast most cancers victims and survivors,” acknowledged Wang, noting that an inhibitor of miR-122, developed by Regulus Therapeutics Inc. in San Diego, is at current in scientific trial as a doable remedy for energy hepatitis C. It has been found to be environment friendly in restoring common insulin manufacturing and suppressing tumor improvement in mouse fashions of breast most cancers.
“These miR-122 inhibitors, which happen to be the first miRNA-based remedy to enter scientific trials, might have a model new use in breast most cancers treatment,” Wang acknowledged.
Uncover additionalResearchers report novel findings for breast most cancers victims with weight issues, diabetes